

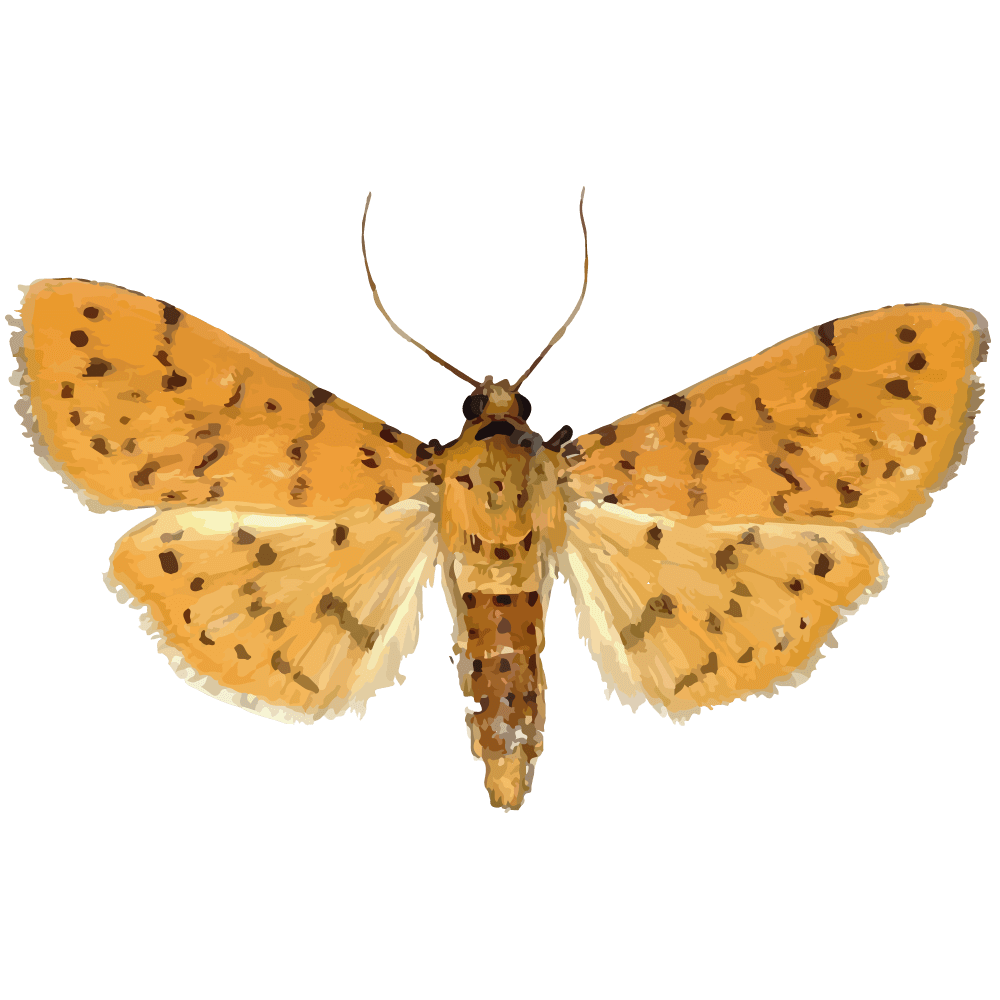
| Latin Name | Conogethes punctiferalis |
| Common Name | fruit borer;yellow peach moth |
| Biology | Adults are nocturnal, exhibiting strong phototaxis and chemotaxis (responding to sugar-vinegar mixtures), laying eggs on fruits, spikes, or leaves of peach, corn, and other plants. Larvae bore into peaches and corn spikes, causing fruit rot, seed shriveling, and damage to sunflower and sorghum. This species completes 4–5 generations annually, overwintering as mature larvae in tree bark fissures or corn stalks. |
| Damage | Primary hosts include peach, plum, apricot, corn, and sunflower. |
| Distribution Regions | East and South Asia |
| Monitoring | Pheromone lures mimic natural sex pheromones to attract male insects into specialized traps for population monitoring and suppression. As a core IPM component, monitoring enables early risk detection and targeted control. Mass trapping reduces mating opportunities to curb offspring populations. Protocols: ●Use only with matched traps. ●15-45 traps/hectare,replace/replenish every 4-6 weeks. ●Wear gloves or wash hands with detergent when switching lure types. ●Refer to trap-specific hanging instructions. |
| Recommended Traps | Delta Trap, Wing Trap |

ご連絡先情報をご提供ください。精密にマッチしたフェロモンソリューションをご提供します。当社の既存ポートフォリオに最適なソリューションが見つからない場合、合成化学チームが分子構造設計から量産まで一貫してカスタム開発を実施いたします。